Mechanical Engineering :: Theory of Machine
-
A system in dynamic balance implies that
-
The example of completely constrained motion is a
-
In involute gears, the pressure angle is
-
The minimum force required to slide a body of weight W on a rough horizontal plane is
-
In a mechanism, the fixed instantaneous centres are those centres which
-
Which of the following statements regarding laws governing the friction between dry surfaces are correct?
-
The frictional torque transmitted in a conical pivot bearing, considering uniform wear, is
-
A combination of kinematic pairs, joined in such a way that the relative motion between the links is completely constrained, is called a
-
A link or element need not to be a rigid body, but it must be a resistant body.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


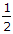 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α 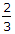 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α 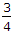 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α