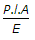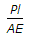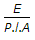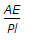Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
The maximum shear stress in a thin spherical shell subjected to an internal pressure (p) is zero.
-
The change in length due to a tensile or compressive force acting on a body is given by (where P = Tensile or compressive force acting on the body, l = Original length of the body, A = Cross-sectional area of the body, and E = Young's modulus for the material of the body)
-
The assumption, generally, made in the theory of simple bending is that
-
The shear force of a cantilever beam of length l carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length is __________ at the fixed end.
-
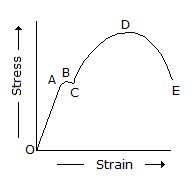
In the below figure, stress is proportional to strain, for the portion
-
The product of Young's modulus (E) and moment of inertia (I) is known as
-
The relation between equivalent length (L) and actual length (l) of a column for both ends fixed is
-
The ratio of maximum shear stress developed in a rectangular beam and a circular beam of the same cross-sectional area is
-
Transverse fillet welds are designed for
-
A beam of triangular section is placed with its base horizontal. The maximum shear stress occurs at


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook