Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite forces, acting tangentially across the resisting section, as a result of which the body tends to shear off across the section, the stress and strain induced is
-
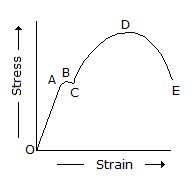
In the below figure, the plastic range occurs
-
The perpendicular distance between the centre lines of the successive rows, is called pitch.
-
The values of equivalent length (L) and actual length (l) of a column for both ends hinged is the same
-
The stiffness of a closely-coiled helical spring is __________ proportional to number of turns.
-
The maximum bending moment of a simply supported beam of span l and carrying a point load W at the centre of beam, is
-
A column of length (l) with both ends fixed may be considered as equivalent to a column of length __________ with one end fixed and the other end free.
-
For biaxial stress, the planes of maximum shear are at right angles to each other and are inclined at 45° to the principal planes.
-
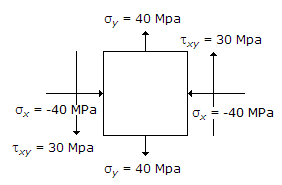
The state of stress at a point in a loaded member is shown in the below figure. The magnitude of maximum shear stress is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

