GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Civil
- A symmetric frame PQR consists of two inclined members PQ and QR, connected at 'Q' with a rigid joint, and hinged at 'P' and 'R'. The horizontal length PR is l. If a weight W is suspended at 'Q', the bending moment at 'Q' is
-
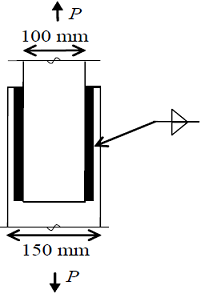
Two plates are connected by fillet welds of size 10 mm and subjected to tension, as shown in the sketch. The thickness of each plate is 12 mm. The yield stress and the ultimate tensile stress of steel are 250 MPa and 410 MPa, respectively. The welding is done in the workshop (Ï’mw = 1.25). As per the Limit State Method of IS 800:2007, the minimum length (rounded off to the nearest higher multiple of 5 mm) of each weld to transmit a force P equal to 270 kN is
- Two soil specimens with identical geometric dimensions were subjected to falling head permeability tests in the laboratory under identical conditions. The fall of water head was measured after an identical time interval. The ratio of initial to final water heads for the test involving the first specimen was 1.25. If the coefficient of permeability of the second specimen is 5-times that of the first, the ratio of initial to final water heads in the test involving the second specimen is
- A layer of normally consolidated, saturated silty clay of 1 m thickness is subjected to one dimensional consolidation under a pressure increment of 20 kPa. The properties of the soil are: specific gravity = 2.7, natural moisture content = 45%, compression index = 0.45, and recompression index = 0.05. The initial average effective stress within the layer is 100 kPa. Assuming Terzaghi's theory to be applicable, the primary consolidation settlement (rounded off to the nearest mm) is
-
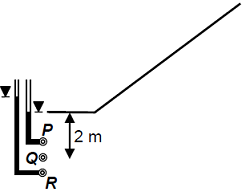
Steady state seepage is taking place through a soil element at Q, 2 m below the ground surface immediately downstream of the toe of an earthen dam as shown in the sketch. The water level in a piezometer installed at P, 500 mm above Q, is at the ground surface. The water level in a piezometer installed at R, 500 mm below Q, is 100 mm above the ground surface. The bulk saturated unit weight of the soil is 18 kN/m3 and the unit weight of water is 9.81 kN/m3. The vertical effective stress (in kPa) at Q is
- The top width and the depth of flow in a triangular channel were measured as 4 m and 1 m, respectively. The measured velocities on the centre line at the water surface, 0.2 m and 0.8 m below the surface are 0.7 m/s, 0.6 m/s and 0.4 m/s, respectively. Using two-point method of velocity measurement, the discharge (in m3/s) in the channel is
- Wheat crop requires 55 cm of water during 120 days of base period. The total rainfall during this period is 100 mm. Assume the irrigation efficiency to be 60%. The area (in ha) of the land which can be irrigated with a canal flow of 0.01 m3/s is
- A water sample has a pH of 9.25. The concentration of hydroxyl ions in the water sample is
- A town is required to treat 4.2 m3/min of raw water for daily domestic supply. Flocculating particles are to be produced by chemical coagulation. A column analysis indicated that an overflow rate of 0.2 mm/s will produce satisfactory particle removal in a settling basin at a depth of 3.5 m. The required surface area (in m2) for settling is
- A two-lane urban road with one-way traffic has a maximum capacity of 1800 vehicles/hour. Under the jam condition, the average length occupied by the vehicles is 5.0 m. The speed versus density relationship is linear. For a traffic volume of 1000 vehicles/hour, the density (in vehicles/km) is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

