GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Civil
-
Two bitumen samples "X and "Y have softening points 45oC and 60oC, respectively. Consider the following statements: I. I Viscosity of "X will be higher than that of "Y at the same temperature.II Penetration value of "X will be lesser than that of "Y under standard conditions.The CORRECT option evaluating the above statements is
- Road roughness is measured using
-
Which of the following errors can be eliminated by reciprocal measurements in differential leveling? I Error due to earth's curvatureII Error due to atmospheric refraction
-
The error in
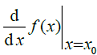 for a continuous function estimated with h = 0.03 using the central difference formula
for a continuous function estimated with h = 0.03 using the central difference formula 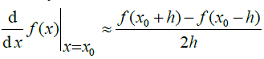 , is 2 * 10-3. The values of x0 and f(x0) are 19.78 and 500.01, respectively. The corresponding error in the central difference estimate for h = 0.02 is approximately
, is 2 * 10-3. The values of x0 and f(x0) are 19.78 and 500.01, respectively. The corresponding error in the central difference estimate for h = 0.02 is approximately - In an experiment, positive and negative values are equally likely to occur. The probability of obtaining at most one negative value in five trials is
- The solution of the ordinary differential equation dy/dx + 2y = 0 for the boundary condition, y = 5 at x = 1 is
- A simply supported beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of intensity w per unit length, on half of the span from one end. The length of the span and the flexural stiffness are denoted as l and EI, respectively. The deflection at mid-span of the beam is
-
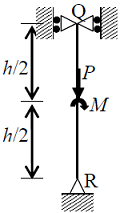
The sketch shows a column with a pin at the base and rollers at the top. It is subjected to an axial force P and a moment M at mid-height. The reaction(s) at R is/are
-
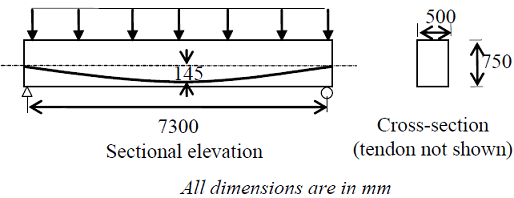
A concrete beam prestressed with a parabolic tendon is shown in the sketch. The eccentricity of the tendon is measured from the centroid of the cross-section. The applied prestressing force at service is 1620 kN. The uniformly distributed load of 45 kN/m includes the self-weight.The stress (in N/mm2) in the bottom fibre at mid-span is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


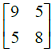 are
are