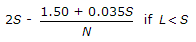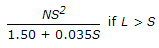Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
The gradients of trace cuts for hilly roads, are kept
-
The width of the right of way in urban area, is kept between 24 m to 60 m for
-
The safe length L of a valley curve for night travel is
-
If the rate of change of the super-elevation along a curved portion of a 7 metre wide road is 1 in 150 and the maximum super-elevation allowed is 1 in 15, the maximum length of the transition curve to be provided at either end, is
-
The full width of land acquired before finalising a highway, alignment is known
-
Retaining walls are generally constructed with dry rubble stones with 60 cm top width and
-
The ability of a driver to stop the vehicle moving with the designed speed, depends upon:
-
To prevent compressive stresses in a rigid concrete pavement, the joint prvoided, is
-
In case of cement concrete pavements, pick up the incorrect statement
-
The radius of curvature provided along a transition curve, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook