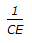Chemical Engineering :: Heat Transfer
-
Crystal size in a continuous crystalliser depends upon the
-
Heat waves
-
Air is best heated with steam in a heat exchanger of
-
Which of the following is generally considered as opaque surface towards radiations?
-
Black liquor generated during paper manufacture is concentrated in a
-
When vaporisation takes place directly at the heating surface, it is called
-
Steam consumption in kg/hr in case of an evaporator is given by (where, C & E are capacity the economy of the evaporator respectively)
-
With increase in temperature, the thermal conductivity of non-metallic amorphous solids
-
Fourier's law applies to the heat transfer by


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook