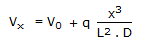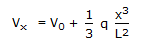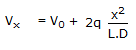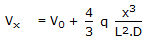Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
With the increase in depth, the hydrostatic pressure in an unaccelerated incompressible fluid (in a constant gravitational field)
-
Flow measurement in an open channel is done by a/an
-
Newton's law of viscosity relates the
-
Applicability of Bernoulli's equation is limited to a/an __________ fluid, that does not exchange shaft work with the surroundings.
-
The equivalent diameter for fluid flow through square cross section channel of side 'x', for pressure drop calculation purpose is given by
-
Hydraulic radius of 6" x 12" cross-section, is __________ inches.
-
Baffles in mixing tanks are provided to
-
Which of the following equations is valid for laminar flow of a fluid through packed bed?
-
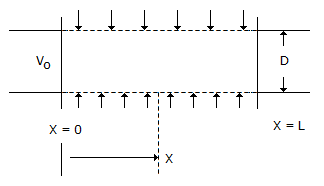
A pipe has a porous section of length L as shown in the figure. Velocity at the start of this section of V0. If fluid leaks into the pipe through the porous section at a volumetric rate per unit area q(x/L)2, what will be axial velocity in the pipe at any x ? Assume incompressible one dimensional flow i.e., no gradients in the radial direction.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook