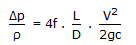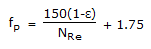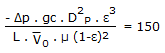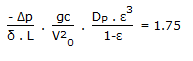Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
Poise is converted into stoke by
-
The fluid velocity varies as the square root of the cylindrical pipe diameter in case of steady state laminar flow at constant pressure drop fo __________ fluid.
-
Kinetic energy of fluid per unit weight represented by the velocity head is given by
-
At a constant speed of the centrifugal pump . it __________ the impeller diameter.
-
The pressure co-efficient is the ratio of pressure forces to __________ forces.
-
Vena-contracta formed during flow of a liquid through an orificemeter has
-
Pick out the Blake-Plummer equation (valid for large NRe) for fluid flow through beds of solids.
-
As per Newton's law of viscosity, the shear stress for a given rate of angular deformation of fluid is proportional to(where, μ = fluid viscosity)
-
Horsepower increase of a centrifugal gas compressor without altering the volumetric flow rate will __________ the gas discharge pressure.
-
In continuous fluidisation


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook