Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
In area meter (e.g., rotameter), with increase in the fluid flow rate, the
-
The buoyant force acting on a floating body is dependent on the
-
A Newtonion fluid is that
-
In case of end to end connection of two or more pipes in series, the __________ each pipe.
-
Which of the following equations applies to the fluid flow through a packed bed for very large Reynolds number ?
-
The flow of gas along a pipe in the direction of decreasing pressure causes decrease in its
-
Centrifugal pump can't be used to pump
-
A stream line is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


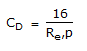
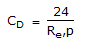
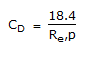
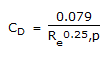
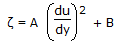 , then the fluid is
, then the fluid is