Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
In case of isentropic flow, the speed of sound in an ideal gas is proportional to (where, T = absolute temperature )
-
Applying a pressure drop across a capillary results in a volumetric flow rate 'Q' under laminar flow conditions. The flow rate for the same pressure drop, in a capillary of the same length but half the radius is
-
Cd, Cc and Cv are related (for flow through an orifice) as (where, Cd = discharge co-efficient
Cc = co-efficient of contraction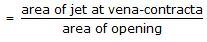
Cv = co-efficient of velocity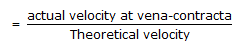 )
) -
In an incompressible fluid, the density is
-
Check valves are used
-
Velocity distribution for flow between two fixed parallel plates
-
An ideal nozzle design aims at
-
Which of the fluid forces are not considered in the Reynold's equation of flow ?
-
A mono pump is a __________ pump.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

