Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
What causes convective acceleration in fluid flow ?
-
The Stoke's stream function applies to the
-
Slugging in a fluidised bed can be avoided by using
-
The ratio of width to depth for the most economical rectangular section in open channel flow is
-
The simple pitot tube measures the __________ pressure.
-
Capacity of a hydraulic accumulator is defined in terms of maximum
-
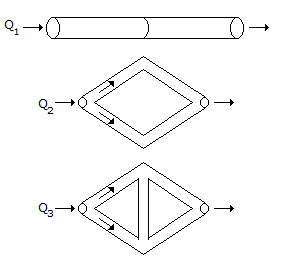
Three piping networks as shown in the figure are placed horizontally. They are made using identical pipe segments and are subjected to the same pressure drop across them. Assuming no pressure losses at junctions, the flow rates across the three networks are related as Q1 : Q2 : Q3.
-
With diminishing cross-sectional area in case of subsonic flow in a converging nozzle, the
-
Boundary layer separation is characterised by one of the conditions given below, where 'Re' is the Reynolds number for the flow. Select the appropriate conditions.
-
Manometers measure the __________ pressure.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

