Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
When dilute aqueous solutions of two salts are mixed, the process is associated with
-
Pick out the correct statement.
-
Chemical engineering thermodynamics is concerned with the __________ in/of chemical processes.
-
An isolated system can exchange __________ with its surroundings.
-
Requisites of a reversible process is that the
-
Fugacity is most helpful in
-
The energy of activation of exothermic reaction is
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
In the reaction; N2 + O2
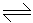 2NO, increasing the pressure will result in
2NO, increasing the pressure will result in -
A cyclic engine exchanges heat with two reservoirs maintained at 100 and 300°C respectively. The maximum work (in J) that can be obtained from 1000 J of heat extracted from the hot reservoir is
|
A.
Like internal energy and enthalphy, the absolute value of standard entropy for elementary substances is zero.
|
|
B.
Melting of ice involves increase in enthalpy and a decrease in randomness.
|
|
C.
The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its pressure.
|
|
D.
Maximum work is done under reversible conditions.
|
|
A.
The chemical potential of a pure substance depends upon the temperature and pressure.
|
|
B.
The chemical potential of a component in a system is directly proportional to the escaping tendency of that component.
|
|
C.
The chemical potential of ith species (μi) in an ideal gas mixture approaches zero as the pressure or mole fraction (xi) tends to be zero at constant temperature.
|
|
D.
The chemical potential of species 'i' in the mixture (μi) is mathematically represented as,
 , where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy. , where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy. |


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

