Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
The heat capacity of most substances is greater for the __________ state.
-
The temperature at which real gases obey the ideal gas law over a wide range of pressure is called the __________ temperature.
-
Elements in a periodic table are arranged in order of their
-
For most salts, the solubility increases with rise in temperature, but the solubility of __________ is nearly independent of temperature rise.
-
The molecules of a liquid which is in equilibrium with its vapor at its boiling point on an average have equal __________ in the two phases.
-
If a solution of eutectic composition is cooled, __________ reaching the eutectic temperature.
-
The density of a gas 'X' is twice that of another gas 'Y'. If the molecular weight of gas 'Y' is 'M'; then the molecular weight of the gas 'X' will be
-
The equilibrium data of component A in the two phases B and C are given below.
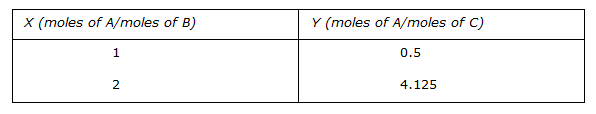
The estimate of Y for X = 4 by fitting a quadratic expression of a form Y = mX2 for the above data is -
Saturated solution of benzene in water is in equilibrium with a mixture of air and vapours of benzene and water at room temperature and pressure. Mole fraction of benzene in liquid is xB and the vapour pressures of benzene and water at these conditions are pvB and pvw respectively. The partial pressure of benzene in air-vapour mixture is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

