Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
Colligative properties of a dilute solution are those which depend entirely upon the
-
For an ideal solution, the total vapor pressure varies __________ with the composition(expressed as mole fraction).
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
Measurement of the amount of dry gas collected over water from volume of moist gas is based on the
-
In physical adsorption, as compared to chemisorption, the
-
The combustion equations of carbon and carbon monoxide are as follows:
C + O2 = CO2, ΔH = - 394 kJ/kg . mole CO + 1/2 O2 = CO2, ΔH = - 284.5 kJ/kg. mole.
The heat of formation of CO is __________ kJ/kg. mole. -
Dissolving a solute in a solvent does not change its
-
A reduction process is accompanied with increase in the
-
The reaction A + B → C has been conducted in a reactor as shown below.
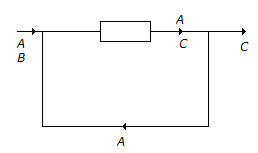
The number of boundaries around which material balance can be written, are -
Heat of transition is the heat evolved or absorbed, when a substance is converted from
|
A.
Atomic heat capacities of the crystalline solid elements are nearly constant and equal to 6.2 kcal/kg-atom according to the law of Petit and Dulong.
|
|
B.
Atomic heat capacities of all solid elements decrease greatly with decrease in temperature, approaching a value of zero at absolute zero temperature, when in the crystalline state.
|
|
C.
Generally, the heat capacities of compounds are lower in the liquid than in the solid state.
|
|
D.
The heat capacity of a heterogeneous mixture is an additive property, but when solutions are formed, this additive property may no longer exist.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

