Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
The heats of vaporisation of CS2, C2H5OH &H2O are 26.8, 38.6 & 40.6 KJ/kg mole respectively. The order of decreasing inter-molecular forces in these liquids is
-
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapor at its boiling point. On an average, the molecules in the liquid and gaseous phases have equal
-
Pure aniline is evaporating through a stagnant air film of 1 mm thickness at 300 K and a total pressure of 100 KPa. The vapor pressure of aniline at 300 K is 0.1 KPa. The total molar concentration under these conditions is 40.1 mole/m3 . The diffusivity of aniline in air is 0.74xl0-5m2/s.The numerical value of mass transfer co-efficient is 7.4 x 10-3. Its units are
-
If 1.5 moles of oxygen combines with aluminium to form Al2O3, then the weight of aluminium (atomic weight = 27 ) used in this reaction is __________ gm.
-
Boiling point of a non-homogeneous mixture of immiscible liquids is __________ that of any one of its separate components.
-
A vapor whose partial pressure is less than its equilibrium vapor pressure is called a __________ vapor.
-
Sometimes, in chemical processes, a part of the outlet stream is rejected as waste in order to keep the impurity level in the system within limits. This phenomenon is termed as the
-
The density of a gas at N.T.P.is 'ρ'. Keeping the pressure constant (i.e. 760 mm Hg), the 3 density of the gas will become
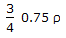 at a temperature of __________ °K
at a temperature of __________ °K -
A gas occupies a volume of 283 c.c at 10°C. If it is heated to 20°C at constant pressure, the new volume of the gas will be __________ c.c.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

