Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
Which of the following terms of Vander Walls equation of state for a non-ideal gas accounts for intermolecular forces ?
-
What is the simplest formula of a compound containing 50% of element A (atomic weight = 10) and 50% of element B (atomic weight = 20) ?
-
The average value of heat of neutralisation of dilute solution of strong acids and strong bases is about __________ kcal/kg.mole of water formed.
-
In a mixture of benzene vapor and nitrogen gas at a total pressure of 900 mm Hg, if the absolute humidity of benzene is 0.2 kg benzene/kg nitrogen, the partial pressure of benzene in mm Hg is
-
For an ideal gas, the compressibility factor
-
In a neutral solution
-
In __________ process, ions of salts react with water to produce acidity or alkalinity.
-
Sodium __________ has inverted solubility curve i.e. its solubility increases with the lowering of temperature.
-
Which of the following has the least (almost negligible) effect on the solubility of a solute in a solvent ?
-
If the partial pressure of the solvent in the vapor phase is equal to the vapor pressure of the solvent at that temperature, then the system is said to be at its

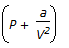

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

