Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
For the gaseous phase reaction, N2 + O2
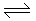 2NO, ΔH = + 80 kJ/kg. mole; the decomposition of NO is favoured by
2NO, ΔH = + 80 kJ/kg. mole; the decomposition of NO is favoured by -
Pick out the correct statement.
-
In case of a solution (not of a solid in a liquid), whose total volume is less than the sum of the volumes of its components in their pure states, solubility is
-
Pure oxygen is mixed with air to produce an enriched air containing 50 volume % of oxygen. The ratio of moles of air to oxygen used is
-
Pick out the correct statement.
-
Normality of a solution does not change with the increase in the
|
A.
A substance existing above its critical temperature is called a saturated vapor.
|
|
B.
A mixture of vapor gas is called saturated, if the equilibrium vapor pressure of the liquid is more than the partial pressure of the vapor at the same temperature.
|
|
C.
Heat added to or given up by a substance at constant temperature is called the sensible heat.
|
|
D.
The end points of a vapor-pressure vs. temperature curve are critical and triple points.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

