Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
Third law of thermodynamics is helpful in
-
Fugacity and pressure are numerically equal, when the gas is
-
Refrigerants commonly used for domestic refrigerators are
-
Solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at the
-
Absolute zero temperature signifies the
-
Specific __________ does not change during a phase change (e.g. sublimation, melting, vaporisation etc.).
-
The equation relating E, P, V and T which is true for all substanes under all conditions is given by
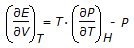 .This equation is called the
.This equation is called the -
For an exothremic reaction
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
|
A.
An ideal liquid or solid solution is defined as one in which each component obeys Raoult's law.
|
|
B.
If Raoult's law is applied to one component of a binary mixture ; Henry's law or Raoult's law is applied to the other component also.
|
|
C.
Henry's law is rigorously correct in the limit of infinite dilution.
|
|
D.
none of these.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

