Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
Work done is a
-
Entropy of the system decreases, when
-
Extensive properties of a thermodynamic system depend upon the __________ of the system.
-
The equation Tds = dE - PdV applies to
-
If an ideal solution is formed by mixing two pure liquids in any proportion, then the __________ of mixing is zero.
-
Near their critical temperatures, all gases occupy volumes __________ that of the ideal gas.
-
The free energy change for a chemical reaction is given by (where, K = equilibrium constant)
-
Free energy, fugacity and activity co-efficient are all affected by change in the temperature. The fugacity co-efficient of a gas at constant pressure ____with the increase of reduced temperature.
-
In the reaction, H2 +I2
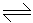 2HI, addition of an inert gas will
2HI, addition of an inert gas will -
The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called the __________ temperature.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

