Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
Gibbs free energy (G) is represented by, G = H - TS, whereas Helmholtz free energy, (A) is given by, A = E - TS. Which of the following is the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
-
Which of the following is an undesirable characteristics of a refrigerant ?
-
"The rate at which a substance reacts is proportional to its active mass and the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of active masses of the reacting substances". This is the
-
What is the ratio of adiabatic compressibility to isothermal compressibility ?
-
The absolute entropy for all crystalline substances at absolute zero temperature is
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
Compressibility factor of a gas is
-
Which of the following is not an extensive property ?
-
Forward reaction will be favoured for the exothermic reaction, represented by CO + H2O
 CO2 + H2, by
CO2 + H2, by


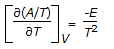

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

