Mechanical Engineering :: Theory of Machine
-
In a steam engine, the link constitutes a
-
The secondary unbalanced force is maximum when the angle of inclination of the crank with the line of stroke is
-
In a kinematic chain, a quaternary joint is equivalent to
-
For dynamic balancing of a shaft
-
The frictional torque transmitted in a conical pivot bearing, considering uniform pressure, is (where R = Radius of shaft, and α = Semi-angle of the cone)
-
Which of the following is an example of a higher pair ?
-
The velocity of a flat-faced follower when it has contact with the flank of a circular arc cam, is given by
-
Which of the following property of the instantaneous centre is correct ?
|
A.
A rigid link rotates instantaneously relative to another link at the instantaneous centre for the configuration of the mechanism considered.
|
|
B.
The two rigid links have no linear velocity relative to each other at the instantaneous centre.
|
|
C.
The velocity of the instantaneous centre relative to any third rigid link is same whether the instantaneous centre is regarded as a point on the first rigid link or on the second rigid link.
|
|
D.
all of the above
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


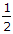 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α 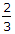 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α 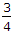 μ W R cosec α
μ W R cosec α