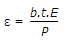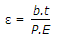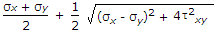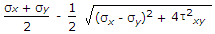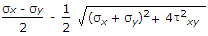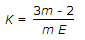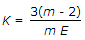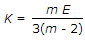Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
A thin cylindrical shell of diameter (d), length (l) and thickness (t) is subjected to an internal pressure (p). The ratio of longitudinal strain to hoop strain is
-
A simply supported beam of length l is loaded with a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length. The maximum deflection is
 and lies at the centre of the beam.
and lies at the centre of the beam. -
When a rectangular bar of length l, breadth b and thickness t is subjected to an axial pull of P, then linear strain (ε) is given by (where E = Modulus of elasticity)
-
When a body is subjected to bi-axial stress i.e. direct stresses (σx) and (σy) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (τxy), then maximum normal stress is
-
In a thick cylindrical shell subjected to an internal pressure (p), the tangential stress across the thickness of a cylinder is
-
The strength of the un-riveted or solid plate per pitch length is
-
For long columns, thevalue of buckling load is __________ crushing load.
-
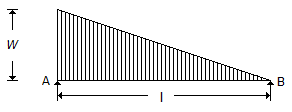
For the beam shown in the below figure, the shear force diagram between A and B is

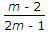
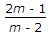

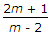

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook