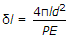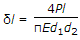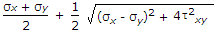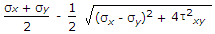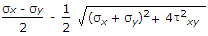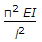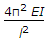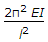Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
A reinforced cement concrete beam is considered to be made of
-
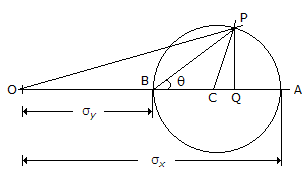
The radius of the Mohr 's circle in the given figure is equal to
-
The extension of a circular bar tapering uniformly from diameter d1 at one end to diameter d2 at the other end, and subjected to an axial pull of P is given by
-
The ratio of bulk modulus to Young's modulus for a Poisson's ratio of 0.25 will be
-
The bending moment diagram for a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a gradually varying load from zero at the free end and w per unit length at the fixed end is a parabolic curve.
-
When a body is subjected to bi-axial stress i.e. direct stresses (σx) and (σy) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (τxy), then minimum normal stress is
-
On one side of a neutral axis of a beam, there is a tensile stress and on the other side of the beam there is a compressive stress.
-
When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (σ), the maximum normal stress is equal to the direct tensile stress.
-
According to Euler's column theory, the crippling load for a column length (l) hinged at both ends, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook