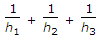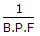Mechanical Engineering :: Heat Transfer,Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
-
The emissive power of a body depends upon its
-
An electric cable of aluminium conductor (k = 240 W/mK) is to be insulated with rubber (k = 0.15 W/mK). The cable is to be located in air (h = 6 W/m2). The critical thickness of insulation will be
-
A cube at high temperature is immersed in a constant temperature bath. It loses heat from its top, bottom and side surfaces with heat transfer coefficients of h1, h2 and h3 respectively. The average heat transfer coefficient for the cube is
-
The dehumidification process, on the psychrometric chart, is shown by
-
The vertical and uniformly spaced lines on a psychrometric chart indicates
-
In case of sensible heating of air, the coil efficiency is given by (where B.P.F. = By-pass factor)
-
The coefficient of performance (C.O.P.) is the reciprocal of the efficiency of a heat engine.
-
The wet bulb temperature at 100% relative humidity is __________ dry bulb temperature.
-
The ratio of the energy absorbed by the body to the total energy falling on it, is called


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook