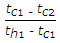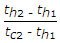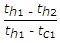Mechanical Engineering :: Heat Transfer,Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
-
The transfer of heat by molecular collision is known as
-
When tc1 and tc2 are the temperatures of cold fluid at entry and exit respectively and th1 and th2 are the temperatures of hot fluid at entry and exit point, and cold fluid has lower heat capacity rate as compared to hot fluid, then effectiveness of the heat exchanger is given by
-
In a psychrometric chart, specific humidity (moisture content) lines are
-
The expression Q = ρ AT4 is called
-
Thermal conductivity of solid metals __________ with rise in temperature.
-
The horizontal and non-uniformly spaced lines on a psychrometric chart indicates
-
A reversible engine has ideal thermal efficiency of 30%. When it is used as a refrigerating machine with all other conditions unchanged, the coefficient of performance will be
-
Which of the following refrigerant is highly toxic and flammable?


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook