GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Mining Engineering
- In the Coward flammability diagram, the respective percentages of methane and oxygen at the nose limit are
- If the transpose of a matrix is equal to its inverse, then the matrix is
- In the Moh's scale of hardness, the minerals in increasing sequence of hardness are
-
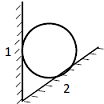
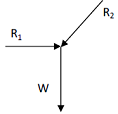
A ball of weight W is supported on smooth walls as shown in the following figure. R1 and R2 are reactions from the walls 1 and 2. The free body diagram of the ball is represented by
- For a 25 mm diameter spherical charge, the maximum allowable charge length in cm is
- Long-hole drilling with crater blasting is used for the construction of
- Rill stoping method is a form of
- Transit theodolite is a
- Incubation period is NOT related to
- The pressure on a phreatic surface is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


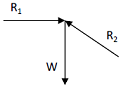 .
.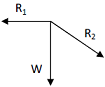 .
.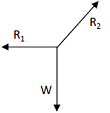 .
. .
.