EEE :: Synchronous Motors
- A synchronous motor working on leading power factor and not driving any mechanical, is known
- Which motor can conveniently operate on lagging as well as leading power factor ?
- The back emf in the stator of a synchronous motor depends on
- Which of the following motors is non-self starling ?
-
In case of a synchronous motor we haveI. LoadII. SpeedIII. DC excitationThe magnitude of stator back emf depends on
- A synchronous motor is switched on to supply with its field windings shorted on themselves. It will
- The purpose of embedding the damper winding in the pole face is to
- A 3 phase, 400 V, 50 Hz salient pole synchronous motor is fed from an infinite bus and is running at no load. Now if the field current of the motor is reduced to zero
-
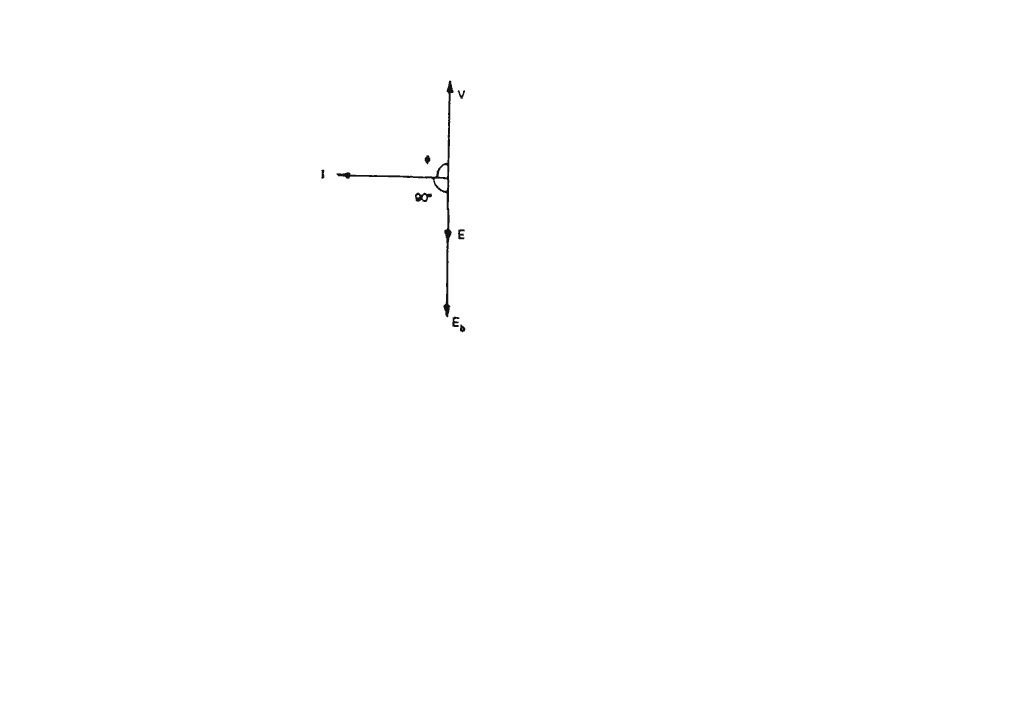
A synchronous motor is connected to supply voltage V drawing current /. Resultant of v and back emf Eb is represented by E in the figure. From this diagram it can be concluded that
- In a synchronous motor if the back emf generated in the armature at no load is approximately equal to the applied voltage, then


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

