ECE :: Microwave Communication
-
The directive gain of a transmitting antenna is
-
A duplexer is used to
-
In a backward wave oscillator the wave
-
A coaxial line has L = 500 nH/m and C = 50 pF/m. The characteristic impedance is
-
The main feature of a parametric amplifier is
-
Assertion (A): PIN diode is commonly used for microwave control.
Reason (R): A PIN diode uses heavily doped p and n materials.
-
In a vacuum tube, the transit time of electron between cathode and anode is important at
-
Assertion (A): A line of length
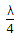 and short circuited at far end has an input impedance of infinity.
and short circuited at far end has an input impedance of infinity.Reason (R): A line of length
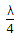 and short circuited at far end behaves as a parallel resonant circuit.
and short circuited at far end behaves as a parallel resonant circuit.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


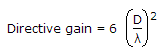
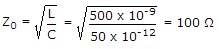 .
.