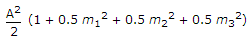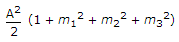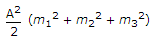ECE :: Communication Systems
-
In a TV receiver antenna the length of reflector rod
-
The modulation index of an FM is changed from 0 to 1. How does the transmitted power change?
-
For a plate-modulated class C amplifier the plate supply voltage is E. The maximum plate cathode voltage could be almost high as
-
In TV systems, equalising pulses are sent during
-
A carrier A cos ωct is modulated by a signal mt A cos ω1t + m2 A cos ω2t + m3 A cos ω3t. The total modulated power is
-
A three stage telephone switching structure is to have 128 input and 128 output terminals. There are 16 first stage and 16 third stage matrices. To avoid blocking the number of intermediate paths required is
-
The main function of a balanced modulator is to
-
Which of the following is not considered as a useful quantity in comparing noise performance of receivers?


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook