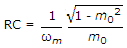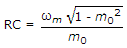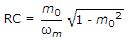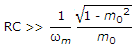ECE :: Communication Systems
-
In a pulsed RADAR, the transmitter is connected to the antenna
-
In a CD, the depth and width of each pit is
-
Which type of modulator amplifier is used in AM transmitter?
-
A digital watch contains
-
In AM increased depth of modulation increases __________ and in FM with increased depth of modulation __________ increases.
-
In a DM system, the granular noise occurs when modulating signal
-
The figure shows a simple detector circuit for amplitude modulated wave v(t) = (1 + m cos ωmt) cost ωct. If the detector is to follow the envelope of modulated wave at all times the extent of modulation m must be less than or equal to m0 where m0 is given by equation
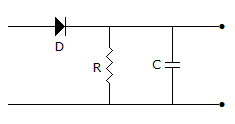
-
Huffman code is also known as redundancy code
-
If each frequency component of f(t) is shifted by p/2, the resulting signal is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook