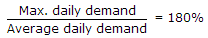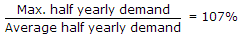Civil Engineering :: Water Supply Engineering
-
The intake opening is generally covered by a screen to prevent entry of debris etc. and its level is kept
-
In rapid sand filters the ratio of length and diameter of the lateral, should not be greater than
-
The maximum permissible hardness for public supplies is
-
Plain chlorination is used for water
-
Water may contain
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
-
For controlling algae, the most commonly used chemical, is
-
The head against which the motor works for lifting water, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook