Civil Engineering :: Water Resources Engineering
-
Water is useful for
-
Knowledge of hydrology is necessary for civil engineers for
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
-
Run off includes
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
-
A soil strata may consist of
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following :
-
If the slope of a line for infiltration capacity curve is
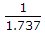 , the value of constant k in Horton's equation of infiltration capacity curve, is
, the value of constant k in Horton's equation of infiltration capacity curve, is -
The equation P - Q = Te φindex for determining the infiltration capacity, was suggested by
|
A.
The amount of water retained on the surface of soil grains by molecular attraction, is known as pellicular water
|
|
B.
The degree of resistance to movement of the pellicular water generally expressed by the surface tension
|
|
C.
The pellicular water held in any soil, is called field capacity
|
|
D.
The portion of the pellicular water absorbed by the root action of the vegetation, is called available moisture
|
|
E.
All the above.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

