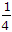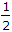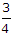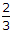Civil Engineering :: Water Resources Engineering
-
The Dupuit formula is based on
-
A well is sunk in an unconfined aquifer having a saturated depth of 100 m. Assuming the equilibrium flow conditions and a homogeneous aquifer and radius of influence to be same, the ratio of discharges at 20 m and 40 m draw downs, is
-
Evaporation losses depend upon
-
Phytometer method is generally used for the measurement of
-
In the estimate of design flood, Dickens assumes that high flood in cumecs, is proportional to catchment area raised to the power
-
For high flood estimates the average value of the constant C in Dicken's formula Q = CA3/4, is
-
Pettis formula Q = C (P.B)5/4 cumecs, is based upon
-
Boston society of Civil Engineer's formula
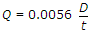 in cumecs/square km is based upon
in cumecs/square km is based upon -
For predicting floods of a given frequency, the best reliable method is
-
The earthen embankments constructed parallel to the river banks at some suitable distance for flood control, are known as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook