Civil Engineering :: Irrigation
-
For a unique design of a channel by Kennedy's theory
-
In a barrage, the crest level is kept
-
For a standing crop, the consumptive use of water is equal to the depth of water
-
The state of the soil when plants fail to extract sufficient water for their requirements, is
-
The field capacity of a soil is 25%, its permanent wilting point is 15% and specific dry unity weight is 1.5. If the depth of root zone of a crop, is 80 cm, the storage capacity of the soil, is
-
Solution of Laplacian equation in three dimensions
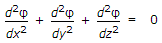 of water in a syphon, is done by
of water in a syphon, is done by -
The length and width of a meander and also the width of the river, vary roughly as
-
Regime conditions in a channel may occur if
-
If the optimum depth of kor watering for a crop is 15.12 cm, the outlet factor for the crop for four week period in hectares per cumec, is
-
If H and d are the water depth and drop in the bed level at a Sarda fall, the width B of the trapezoidal crest, is given by


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

