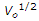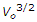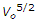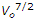Civil Engineering :: Irrigation
-
The scour depth D of a river during flood, may be calculated from the Lacey's equation
-
If V0 is the critical velocity of a channel, its silt transporting power, according to Kennedy, is proportional to
-
The useful moisture of soil, is equal to its
-
Canals taken off from ice-fed perennial rivers, are known
-
The down stream expansion head of a guide bank is extended to subtend an angle at the centre, equal to
-
Trial procedure of canal design by Kennedy's theory is based upon the equation
-
The main cause of silting up a channel,
-
In north Indian Plains, optimum depth of kor watering for wheat, is
-
Bed bars in a canal are provided
-
The most suitable location of a canal head work, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook