Civil Engineering :: Hydraulics
-
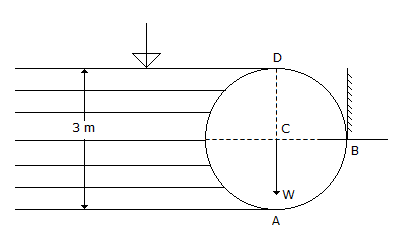
A cylinder 3 m in diameter and 4 m long retains water one side as shown in the below figure. If the weight of the cylinder is 2000 kgf, the horizontal reaction at B is
-
Inside pressure in a hollow soap bubble in the air is : (where d is the diameter of the bubble)
-
The momentum correction factor (β) for the viscous flow through a circular pipe is
-
A piezometer opening in pipes measures
-
An independent mass of a fluid does not posses
-
While applying the Bernoulli's equation \([\frac { p} { w } \) + z +\( \frac { V^2} { 2 g} \)]= total head, the work any section done on the flow system, if any
-
Discharge Q over a rectangular weir of length L and height H, is given by the equation
-
A short tube mouthpiece will not run full at its outlet if the head under which the orifice works, is
-
Hydrostatic pressure on a dam depends upon its
-
When two layers of a fluid separated by dy move over the other with a difference of velocity dv, causes a shearing stress
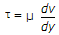 , where u is known as
, where u is known as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

