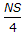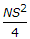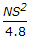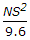Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
Any gradient on a road is said to be an exceptional gradient, if it is
-
For the administration of road transport, a Motor Vehicle Act was enacted in
-
The absolute minimum sight distance required for stopping a vehicle moving with a speed of 80 km ph, is
-
Along high ways confirmatory route markers are generally fixed
-
Length of vehicles does not affect
-
Road width 8.8 m of two lane National highways or State highways in mountainous terrain
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
-
Transverse joints are provided at distances varying from
-
If N is the algebraic difference of grades, S is the minimum sight distance in metres, the length (L) of a summit curve is
-
If N is the net difference of grades, S is the minimum overtaken sight distance in metres, the length (L) of a summit curve, is
|
A.
Long tangent sections exceeding 3 km in length should be avoided
|
|
B.
Curve length should be at least 150 metres for a deflection angle of 5 degress
|
|
C.
For every degree decrease in the deflection angle, 30 metre length of curve to be increased
|
|
D.
If the deflection angle is less than 1°, no curve is designed
|
|
E.
All the above.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook