Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
If C is basic capacity per lane, V is velocity in km/hour, S is stopping distance pluslength of the vehicles in metres, the formula
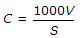 is applicable to
is applicable to -
First operation during the detailed survey of a hill road, is
-
The period of long term plan for the development of roads in India, known as Bombay Plan (Aug. 1958), is
-
According to Highway Research Board of U.S.A. practical land width, is
-
Design of flexible pavements is based on
-
The efficiency of the brakes of a vehicle depends upon
-
The type of transition curves generally provided on hill roads, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

