Civil Engineering :: GATE Exam Questions
-
The span (s) to be loaded uniformly for maximum positive (upward) reaction at support P, as shown in the figure below, is (are)
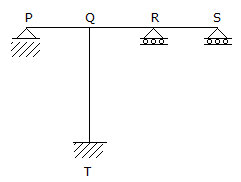
-
Mechanical stabilization requires :
-
The disinfection efficiency of chlorine in water treatment
-
Chlorine is some times used in sewage treatment
-
The deflection of a cantilever beam at free end b applied with a moment M at the same point is :
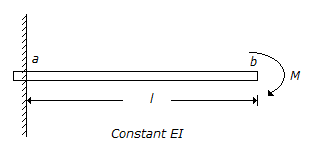
-
A saturated clay stratum draining both at the top and bottom undergoes 50 percent consolidation in 16 years under an applied load. If an additional drainage layer were present at the middle of the clay stratum, 50 percent consolidation would occur in
-
Water flows at a rate of 10 m3/s in a rectangular channel 3 m wide. The critical depth of flow is
-
Coagulation-flocculation with alum is performed :
-
Blue baby disease (methaemoglobinemia) in children is caused by the presence of excess
-
Breakpoint chlorination of water involves addition of chlorine in an amount sufficient to:


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

