Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
The equilibrium data of component A in the two phases B and C are given below.
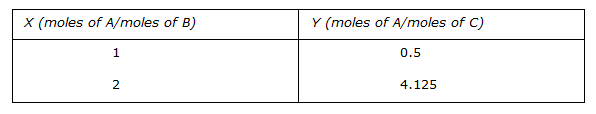
The estimate of Y for X = 4 by fitting a quadratic expression of a form Y = mX2 for the above data is -
Saturated solution of benzene in water is in equilibrium with a mixture of air and vapours of benzene and water at room temperature and pressure. Mole fraction of benzene in liquid is xB and the vapour pressures of benzene and water at these conditions are pvB and pvw respectively. The partial pressure of benzene in air-vapour mixture is
-
The percentage ratio of the partial pressure of the vapor to the vapor pressure of the liquid at the existing temperature is
-
The atomic weight of helium is 4 times that of hydrogen. Its diffusion rate as compared to hydrogen will be __________ times.
-
Osmotic pressure exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving one gram mole of a solute in 22.4 litres of a solvent at 0°C will be __________ atmosphere.
-
In general, the specific heats of aqueous solutions __________ with increase in the concentration of the solute.
-
The ratio of existing moles of vapor per mole of vapor free gas to the moles of vapor that would be present per mole of vapor free gas, if the mixture were saturated at the existing temperature & pressure, is termed as the
-
No cooling occurs, when an ideal gas undergoes unrestrained expansion, because the molecules
-
With increase in the solute concentration, the specific heat of aqueous solutions


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

