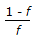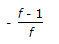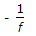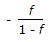Chemical Engineering :: Mass Transfer
-
Flights in a rotary dryer are provided to
-
If f = moles of vapour present per mole of feed, then the slope of feed line is (Mcabe-Thiele method)
-
If the solubilities of different components (in a liquid-liquid extraction system) increase with rise in temperature, then the temperature above which they dissolve completely is known as the critical solution temperature (CST or consolute temperature). If solubilities increase with decrease in temperature, then CST is the temperature below which they dissolve completely. If a binary system has no critical solution temperature, it implies that
-
The rate of mass transfer is not dependent upon the
-
At equilibrium the concentration of water in vapour phase (C*)in kg/m3 of air space and the amount of water (m) adsorbed per kg of dry silica gel are related by, C* = 0.0667m. To maintain dry conditions in a room of air space 100m3 containing 2.2 kg of water vapour initially, 10 kg of dry silica gel is kept in the room. The fraction of initial water remaining in the air space after a long time (during which the temperature is maintained constant) is
-
Dry bulb temperature of unsaturated air is more than its __________ temperature.
-
For the case of flow of air past a wet bulb thermometer (air water vapour system), the approximate value of h2/ky.Cz is around
-
The reciprocal of stripping factor is termed as
-
Ponchan-Savarit method analyses the fractional equipment based on
-
The binary diffusivity in gases at atmospheric conditions is about


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook