Chemical Engineering :: Heat Transfer
-
In a heat exchanger with steam outside the tubes, a liquid gets heated to 45°C, when its flow velocity in the tubes is 2 m/s. If the flow velocity is reduced to 1 m/s, other things remaining the same, the temperature of the exit liquid will be
-
For a liquid in laminar flow through a very long tube, when the exit fluid temperature approaches the wall temperature, the equation to be used is
-
Multiple effect evaporation accounts for
-
In case of a supercooled solution, which is on the verge of crystallisation, the free energy of the solution as compared to that of the solid is
-
Maximum water velocity in tubes of a 1-2 shell and tube heat exchanger may be around __________ metres/second.
-
In Biot number, the characteristic length used is the ratio of the __________ of the solid.
-
Which of the following is the most widely used heat insulating material for pipelines carrying steam ?
-
Heat transfer co-efficient equation for forced convection, Nu = 0.023 Re0.8 . Prn, is not valid, if the value of
-
Which is the best tube arrangement (in a shell and tube heat exchanger) if the fluids are clean and non-fouling ?
-
In case of a multipass shell and tube heat exchanger, the temperature drop in the fluid


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


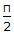 Gz
Gz 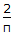 Gz
Gz