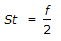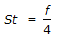Chemical Engineering :: Heat Transfer
-
Crystallisation of solids from a homogeneous solution is a/an __________ process.
-
A multiple effect evaporator has a capacity to process 4000 kg of solid caustic soda per day, when it is concentrating from 10% to 25% solids. The water evaporated in kg per day is
-
Heat transfer in the laminar sublayer in case of a liquid flowing through a pipe, is mostly by
-
Among liquids, water has a comparatively high value of thermal conductivity, due to its
-
Reynold's analogy states that (where, St = Stanton number f = friction factor)
-
For evaporation of viscous solution in a multiple effect evaporator, the prefered feeding scheme is
-
The film thickness for laminar film condensation on vertical surface __________ from top to bottom.
-
In case of a multipass shell and tube heat exchanger, providing a baffle on the shell side __________ the heat transfer rate.
-
The local surface conductance for laminar film condensation on vertical surface is (where, t = film thickness)


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook