Chemical Engineering :: Heat Transfer
-
For large heat transfer area requirement, shell and tube heat exchanger is preferred, because it
-
Out of the following four assumptions used in the derivation of the equation for LMTD
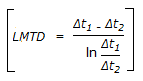 , which one is subject to the largest deviation in practice ?
, which one is subject to the largest deviation in practice ? -
Heat flux increases with temperature drop beyond the Leiden frost point in the plot of heat flux vs. temperature drop for a boiling liquid, because
-
Resistance to heat flow by conduction is proportional to (where, t & ρ are thickness & density of the material respectively and A = area normal to the direction of heat flow. )
-
Temperature profile in steady state heat transfer is
-
For the same heat load and mass flow rate in the tube side of a shell and tube heat exchanger, one may use multipass on the tube side, because it
-
When vaporisation takes place through a blanketting film of gas, the phenomenon is termed as __________ boiling.
-
Minimum recommended baffle spacing in a shell and tube heat exchanger is about (where, D = shell diameter)
-
Stefan-Boltzman law which describes the radiation heat transfer states that, it is proportional to (where, t = temperature in °C T = absolute temperature in ° K )
-
The Nusselt number for fully developed (both thermally and hydrodynamically) laminar flow through a circular pipe, where the wall heat flux is constant, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

