Chemical Engineering :: Fuels and Combustion
-
The reaction, C + CO2
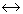 2CO, taking place during coal gasification is called the __________ reaction.
2CO, taking place during coal gasification is called the __________ reaction. -
The maximum percentage of CO2 in a flue gas (from a carbonaceous fuel) can be
-
A good quality coal should have
-
High amount of sulphur and phosphorous in coke causes
-
The difference between total carbon and fixed carbon of coal will be minimum in case of
-
The maximum adiabatic flame temperature is attained, when the fuel is burnt with
-
Grindability index of a coal is 100. It implies that the
-
The cooling medium used in dry quenching of coke is
-
A particular coal is said to be free burning when it
-
Gobar gas is produced by the __________ of 'gobar' (cow dung).


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

