Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
A body is subjected to a direct tensile stress of 300 MPa in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress of 200 MPa. The maximum normal stress will be
-
A simply supported beam 'A' of length l, breadth b, and depth d carries a central point load W. Another beam 'B' has the same length and depth but its breadth is doubled. The deflection of beam 'B' will be __________ as compared to beam 'A'.
-
The moment of resistance of a balanced reinforced concrete beam is based on the stresses in
-
The load at which the column just buckles, is known as
-
The Rankine's constant for a mild steel column with both ends hinged is
-
The rectangular beam 'A ' has length l, width b and depth d. Another beam 'B' has the same width and depth but length is double that of 'A'. The elastic strength of beam 'B' will be __________ as compared to beam A.
-
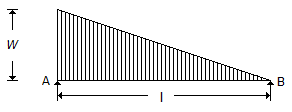
A simply supported beam with a gradually varying load from zero at B and w per unit length at A is shown in the below figure. The shear force at B is equal to
-
A tensile test is performed on a round bar. After fracture, it has been found that the diameter remains approximately same at fracture. The material under test was
-
In a simply supported beam carrying a uniformly distributed load w per unit length, the point of contraflexure
-
Modulus of rigidity may be defined as the ratio of


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

