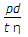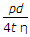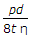Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
If percentage elongation of a certain specimen made of a material 'A' under tensile test is 30% and the percentage elongation of a specimen with same dimensions made of another material 'B' is 40%, then material 'B' is more ductile than material 'A'.
-
Factor of safety is defined as the ratio of
-
The value of equivalent length is taken to be half of the actual length of a column with one end fixed and the other end free.
-
The shear force diagram of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length will be
-
Whenever some external system of forces acts on a body, it undergoes some deformation. As the body undergoes some deformation, it sets up some resistance to the deformation. This resistance per unit area to deformation, is called
-
The longitudinal stress in a riveted cylindrical shell of diameter (d), thickness (t) and subjected to an internal pressure (p) is
-
Two solid shafts 'A' and 'B' are made of the same material. The shaft 'A' is of 50 mm diameter and shaft 'B' is of 100 mm diameter. The strength of shaft 'B' is __________ as that of shaft A.
-
In calculating the strength of a riveted joint in tearing, shearing and crushing, the


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook