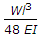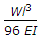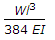Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
A uniformly distributed load may be assumed to behave like a point load at the centre of gravity of the load for all sorts of calculations.
-
The shear force in the centre of a simply supported beam carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length, is
-
When a change in length takes place, the strain is known as
-
The maximum bending moment of a simply supported beam with central point load lies at the point of loading.
-
When the shear force diagram between any two points is an inclined straight line, it indicates that there is a uniformly varying load between the two points.
-
The maximum deflection of a fixed beam of length l carrying a total load W uniformly distributed over the whole length is
-
The pull required to tear off the plate per pitch length is (where p = Pitch of rivets, t = Thickness of plates, and σt, τ and σc = Permissible tensile, shearing and crushing stresses respectively)
-
When a beam is subjected to bending moment, the stress at any point is __________ the distance of the point from the neutral axis.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook