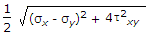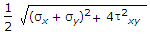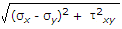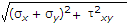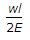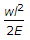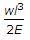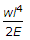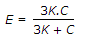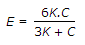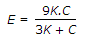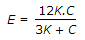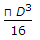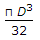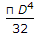Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
The design of thin cylindrical shells is based on
-
When a body is subjected to bi-axial stress i.e. direct stresses (σx) and (σy) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (τxy), then maximum shear stress is
-
The pull required to crush the rivet per pitch length is
-
When a bar of length l and diameter d is rigidly fixed at the upper end and hanging freely, then the total elongation produced in the bar due to its own weight is (where w = Weight per unit volume of the bar)
-
The deformation of the bar per unit length in the direction of the force is known as
-
Which of the following statement is correct?
-
The relation between Young's modulus (E), shear modulus (C) and bulk modulus (K) is given by
-
The volumetric strain is the ratio of the


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook